Loan approval process sets the stage for your financial journey, uncovering the secrets to navigating the complex world of loans with swagger and confidence. Get ready to dive into the nitty-gritty details and come out on top!
From understanding the stages of approval to acing the underwriting process, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to secure that coveted approval.
Loan Approval Process Overview
When applying for a loan, there are several stages involved in the approval process. Lenders carefully evaluate various factors to determine the applicant’s eligibility and creditworthiness. Understanding the key criteria and documentation required can help streamline the process and increase the chances of approval.
Stages of the Loan Approval Process
- Lender Evaluation: The lender will assess the applicant’s credit score, income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratio to determine their financial stability.
- Application Submission: The applicant must complete a loan application form and provide necessary documentation, such as proof of income, identification, and bank statements.
- Underwriting: The lender will review the application, documentation, and credit report to make a final decision on whether to approve the loan.
- Approval or Rejection: Based on the evaluation, the lender will either approve the loan, offer a different loan amount/terms, or reject the application.
Key Criteria Considered by Lenders
- Credit Score: A high credit score indicates a strong credit history and increases the likelihood of loan approval.
- Income and Employment: Lenders look for stable income and employment to ensure the borrower can repay the loan.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: A lower ratio shows that the borrower has manageable debt compared to their income.
Documentation Required for a Loan Application
- Proof of Income: Pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements to verify the applicant’s income.
- Identification: Government-issued ID, such as a driver’s license or passport, to confirm the applicant’s identity.
- Bank Statements: Statements showing the applicant’s savings, checking accounts, and any other assets.
Timeline for the Loan Approval Process
- Application Submission: Typically takes a few days to complete and submit all required documentation.
- Underwriting Process: Can vary from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the lender’s workload and complexity of the application.
- Approval Decision: Once underwriting is complete, the lender will notify the applicant of the approval or rejection, usually within a week.
Pre-Approval Phase
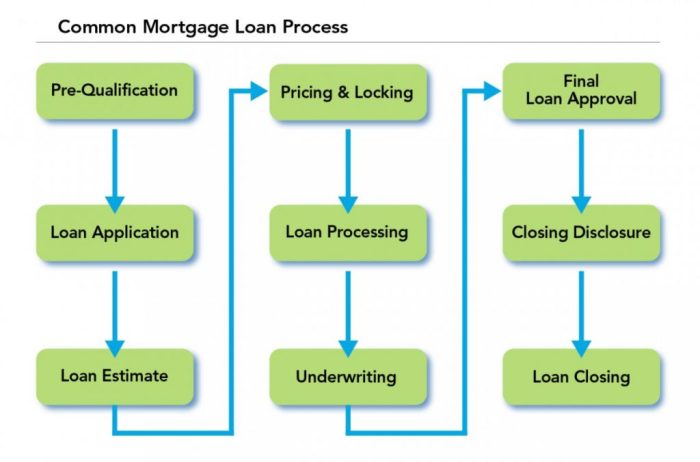
In the loan approval process, the pre-approval phase is crucial as it helps you determine how much you can borrow and sets you up for a smoother home buying experience.
Importance of Pre-Approval
- Pre-approval gives you a clear picture of your budget and helps you shop within your means.
- Sellers take you more seriously when you have a pre-approval letter, increasing your chances of securing the property you want.
Difference between Pre-Qualification and Pre-Approval
- Pre-qualification is an estimate of how much you might be able to borrow based on self-reported information, while pre-approval involves a thorough review of your financial background by a lender.
- Pre-qualification is not as strong as pre-approval since it doesn’t involve verification of your financial status.
Steps for Getting Pre-Approved
- Collect financial documents such as pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements.
- Submit a loan application to a lender for review.
- Undergo a credit check and provide any additional documentation requested by the lender.
- Receive a pre-approval letter outlining the loan amount you qualify for.
Tips for Improving Your Chances of Getting Pre-Approved
- Work on improving your credit score by paying bills on time and reducing debt.
- Avoid making any major purchases or opening new lines of credit before getting pre-approved.
- Provide all required documents promptly to expedite the pre-approval process.
- Consider working with a reputable mortgage broker who can help guide you through the pre-approval process.
Application Submission: Loan Approval Process

When it comes to submitting a loan application, it’s essential to follow the process carefully to increase your chances of approval. Here’s a breakdown of what you need to know:
Filling out the Loan Application
To fill out a loan application accurately, make sure to provide all the required information truthfully and completely. This includes personal details, financial information, employment history, and the purpose of the loan. Double-check all entries to avoid any errors that could delay the process.
Importance of Providing Necessary Documentation
Accompanying your loan application with all necessary documentation is crucial. This may include pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements, and any other relevant financial records. Providing these documents helps lenders verify your information and make a well-informed decision regarding your loan approval.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
– Failing to provide all required information on the application form.
– Submitting incomplete or inaccurate information.
– Neglecting to include all necessary documentation.
– Waiting until the last minute to submit the application, leading to potential delays.
– Not reviewing the application before submission for errors or missing information.
Remember, a well-prepared and accurately filled-out loan application, accompanied by all necessary documentation, can significantly improve your chances of getting approved for the loan you need.
Underwriting Process
When a loan application reaches the underwriting process, it means that the lender is taking a closer look at the applicant’s financial situation to assess their creditworthiness. This step involves a thorough review of the borrower’s ability to repay the loan and the overall risk involved in lending to them.
Assessing Creditworthiness
- Lenders evaluate an applicant’s creditworthiness by checking their credit score and credit history. A higher credit score indicates a lower risk for the lender, making it easier to secure a loan.
- They also look at the borrower’s debt-to-income ratio, which shows how much of their income goes towards paying off debts. A lower ratio is preferred as it indicates a better ability to manage additional debt.
- Previous loan repayment history and any outstanding debts are also considered during the assessment process.
Role of Income Verification
- Income verification is a crucial part of the underwriting process as it helps lenders determine if the applicant has a stable source of income to repay the loan.
- Applicants may be required to provide pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements to verify their income. Self-employed individuals may need to provide additional documentation to prove their income.
- Lenders typically look for consistent and verifiable income sources to ensure that the borrower can meet their loan obligations.
Navigating Challenges
- One common challenge during the underwriting process is if the applicant has a low credit score. In such cases, they may need to provide additional documentation or find a co-signer to strengthen their application.
- Another challenge could be insufficient income to debt ratio, which may require the applicant to explore other loan options or reconsider the loan amount they are applying for.
- Being proactive and transparent with the lender about any potential challenges can help applicants navigate through the underwriting process more smoothly.
Approval or Rejection
When it comes to loan approval decisions, there are several factors that lenders take into consideration. These factors can vary depending on the type of loan and the lender’s specific criteria. Understanding these factors can help you improve your chances of getting approved for a loan.
Factors Influencing Loan Approval
- Your Credit Score: One of the most important factors in determining loan approval is your credit score. Lenders use this to assess your creditworthiness and determine the risk of lending to you.
- Income and Employment History: Lenders will look at your income and employment history to ensure that you have a stable source of income to repay the loan.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: This ratio compares your monthly debt payments to your monthly income. Lenders use this to evaluate your ability to manage additional debt.
- Collateral: For secured loans, the value of the collateral you provide can impact the approval decision. Lenders may require collateral to mitigate their risk.
Reasons for Loan Application Rejection
- Low Credit Score: A low credit score can result in a loan application being rejected, as it indicates a higher risk for the lender.
- Insufficient Income: If your income is not enough to cover the loan payments, lenders may reject your application.
- High Debt-to-Income Ratio: A high debt-to-income ratio can signal that you may struggle to repay the loan, leading to rejection.
- Unstable Employment History: Lenders prefer borrowers with a stable employment history, so frequent job changes or gaps in employment could lead to rejection.
Options After Loan Rejection, Loan approval process
- Review Your Credit Report: Check for any errors on your credit report that may have led to the rejection and address them.
- Improve Your Credit Score: Work on improving your credit score by making timely payments and reducing debt.
- Apply with a Co-Signer: If your credit or income is not strong enough, consider applying with a co-signer who has better financial credentials.
Tips for Loan Approval
- Check Your Credit Report Regularly: Monitor your credit report for errors and take steps to improve your credit score.
- Reduce Debt: Lowering your debt-to-income ratio can improve your chances of getting approved for a loan.
- Provide Accurate Information: Make sure to provide accurate and up-to-date information on your loan application to avoid any discrepancies.
